Section 1.26
Camshaft Gear Assembly Series 60 Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Model
Series 60 EGR uses a camshaft gear assembly. Camshaft, camshaft drive gear and camshaft gear cover are the indivual parts part of this assembly. The camshaft gear assembly is located on top of the cylinder head and is removed and installed as an assembly. The camshaft actuates the intake and exhaust valves and injector operating mechanism. See Figure "Camshaft and Related Parts" .
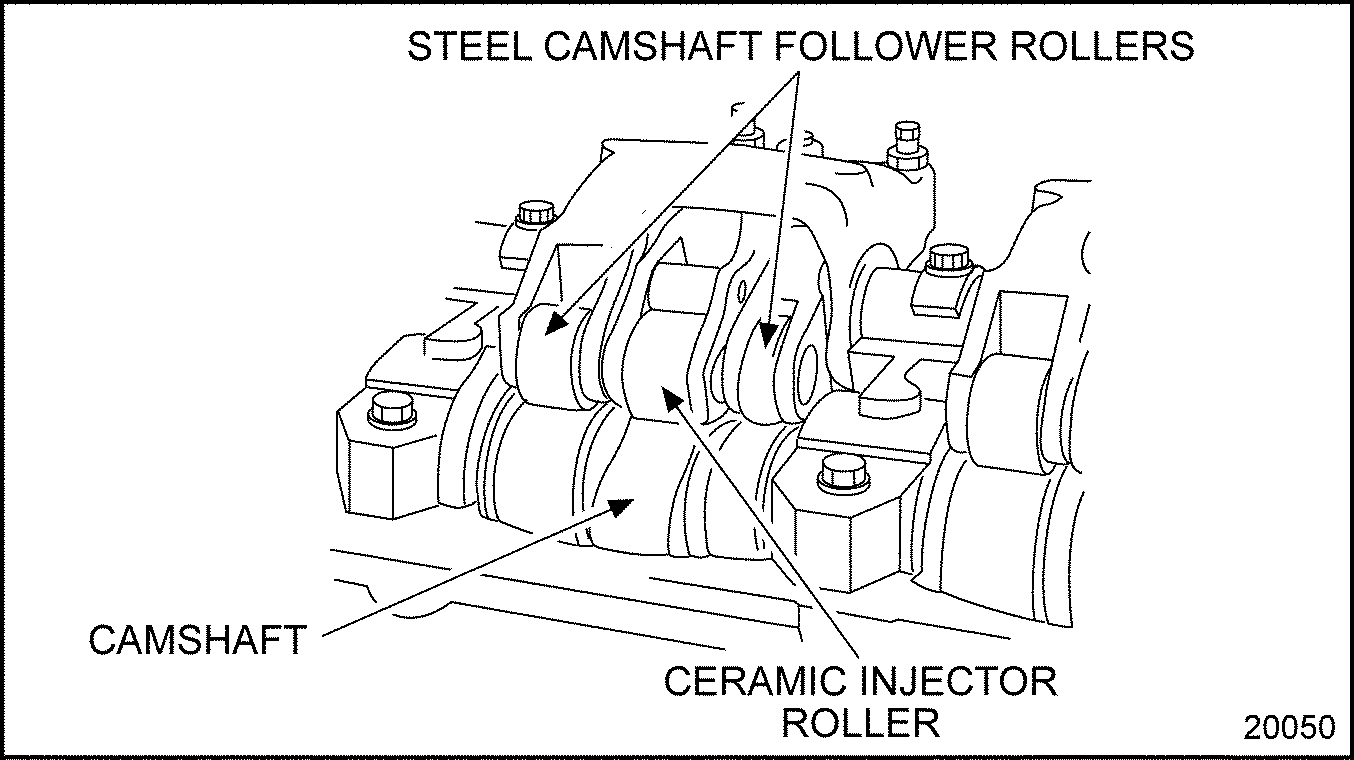
Figure 1. Camshaft and Related Parts
The camshaft is supported by seven bearing assemblies, consisting of precision-type, replaceable bearing shell inserts that are split at their center lines. Current non-tin-plated production bearing shells are identified by their shiny aluminum color. Current tin-plated service bearing shells have a dull gray sheen. The lower bearing shell is positioned in a saddle that is integral with the cylinder head. The upper bearing shell is held in place by a machined camshaft cap. Upper and lower bearing shells are identical and have locating tangs and oil holes. Only the upper bearing shell oil holes index with oil supply holes in the camshaft caps. These camshaft caps are precision line-bored after assembly to the cylinder head.
Note: Caps are NOT interchangeable once the head is finished. Caps are numbered and must NOT be interchanged with other caps of the same part number from stock or from a different cylinder head. See Figure "Camshaft Assembly and Related Parts" .

|
1. Seal |
7. Camshaft Cap Bolt |
|
2. Camshaft Gear |
8. Stud |
|
3. Bolt |
9. Camshaft Bearing Caps |
|
4. Camshaft Gear Cover |
10. Camshaft |
|
5. Seal |
11. Cylinder Head |
|
6. Key |
Figure 2. Camshaft Assembly and Related Parts
The No. 4 camshaft cap is secured to the cylinder head with three bolts; cap numbers 2, 3, 5, and 6 use two bolts each. Caps one and seven have a stud and one bolt each. The stud and nut arrangement on the end caps (1 and 7) allows rocker arm shaft removal without disturbing the gasket eliminator seal from the end camshaft caps to the cylinder head. There are four different camshaft cap configurations. Only the intermediate caps No. 2, 3, 5, and 6 are identical but must not be interchanged during re-assembly. See Figure "Camshaft Bolt and Cap Location" .

|
1. Camshaft Cap Bolt (13) |
2. Camshaft Cap Stud and Nut (2) |
Figure 3. Camshaft Bolt and Cap Location
Note: Caps are NOT interchangeable once the head is finished. Caps are numbered and must NOT be interchanged with other caps of the same part number from stock or from a different cylinder head. See Figure "Camshaft Assembly and Related Parts" .
The camshaft is driven by a camshaft drive gear, located in the camshaft gear cover assembly on top of the gear case, and is driven, through a series of intermediate gears, by the crankshaft timing gear. Refer to "1.24.2.1 Check Engine Timing" for gear train information and camshaft drive gear lash measurement and adjustment procedures. See Figure "Engine Gear Series 60 EGR" .

Figure 4. Engine Gear Series 60 EGR
A cover is provided at the rear end of the camshaft and is secured to the No. 7 camshaft bearing cap and the cylinder head by three bolts. See Figure "Rear Camshaft Access Cover" .
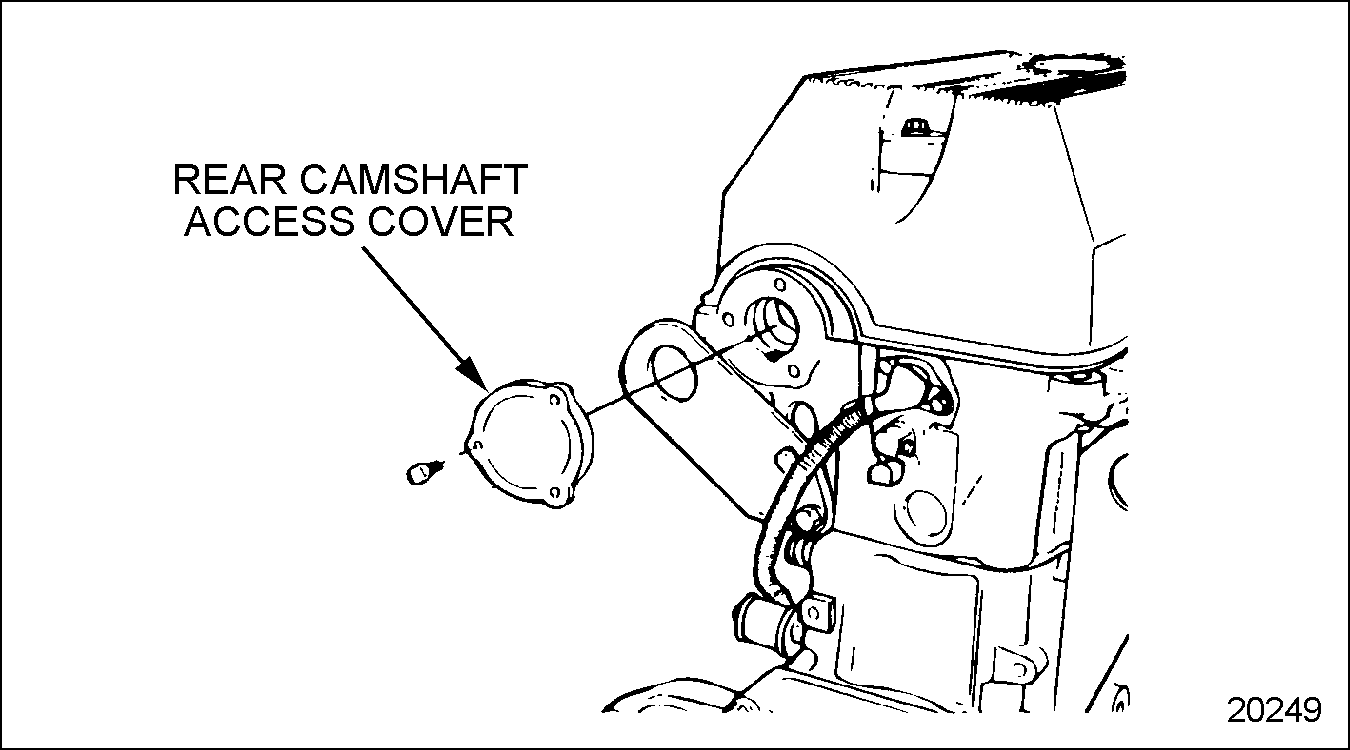
Figure 5. Rear Camshaft Access Cover
Vertical oil passages at the front and rear of the cylinder head deliver oil from the cylinder block front and rear oil galleries to the No. 1 and 7 lower camshaft bearing saddles. From there, the oil is directed upward ( through the enlarged stud hole) to the No. 1 and 7 upper bearing caps. A drilled passage in each of these caps exits at the rocker arm shaft seat area, where it indexes with a hole in each rocker arm shaft. The rocker arm shafts have internal oil passages that deliver oil to the rocker arm bushings and intermediate upper camshaft bearings. Some of the oil supplied to the rocker arm bushing passes through the oil hole in the bushing to the rocker arm. The rocker arm is drilled to supply oil to the camshaft follower, roller pin, and bushing. The rocker arm is also drilled to supply oil to the valve adjusting screw, valve button, retainer clip, intake, and exhaust valve stems and the fuel injector follower. The No. 4 camshaft cap is “Y” drilled, forming an oil path connection between the front and rear rocker arm shafts, to ensure complete lubrication. See Figure "Cylinder Head Lubrication Schematic" .
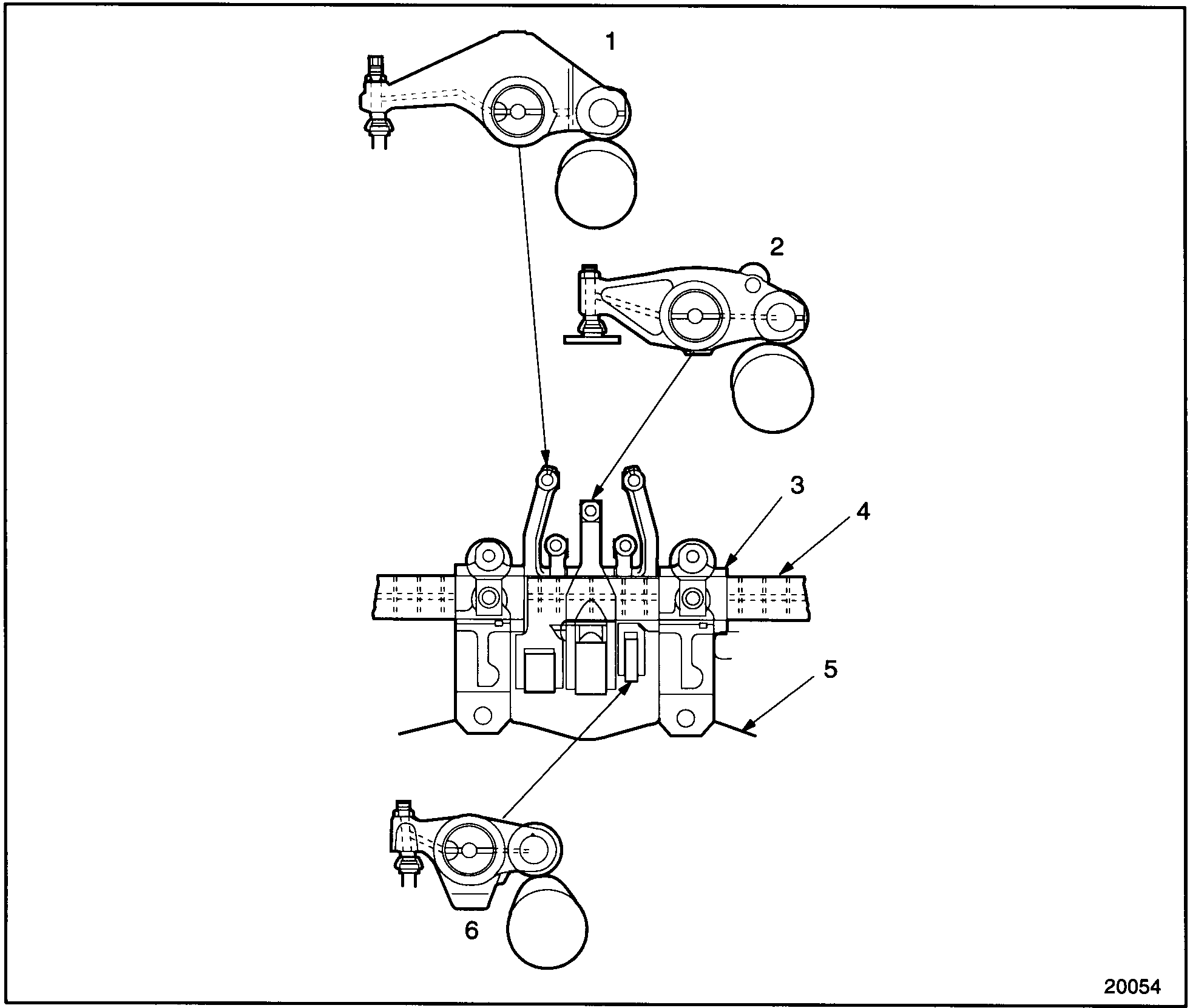
|
1. Rocker Arm, Exhaust Valve |
4. Rocker Arm Shaft |
|
2. Rocker Arm, Fuel Injector |
5. Cylinder Head |
|
3. Camshaft Cap |
6. Rocker Arm, Intake Valve |
Figure 6. Cylinder Head Lubrication Schematic
Section 1.26.1
Repair or Replacement of Camshaft Gear Assembly
To determine if repair or replacement of the camshaft gear assembly is neccessary, perform the following procedure: see Figure "Flowchart for Repair or Replacement of Camshaft Gear Assembly" .
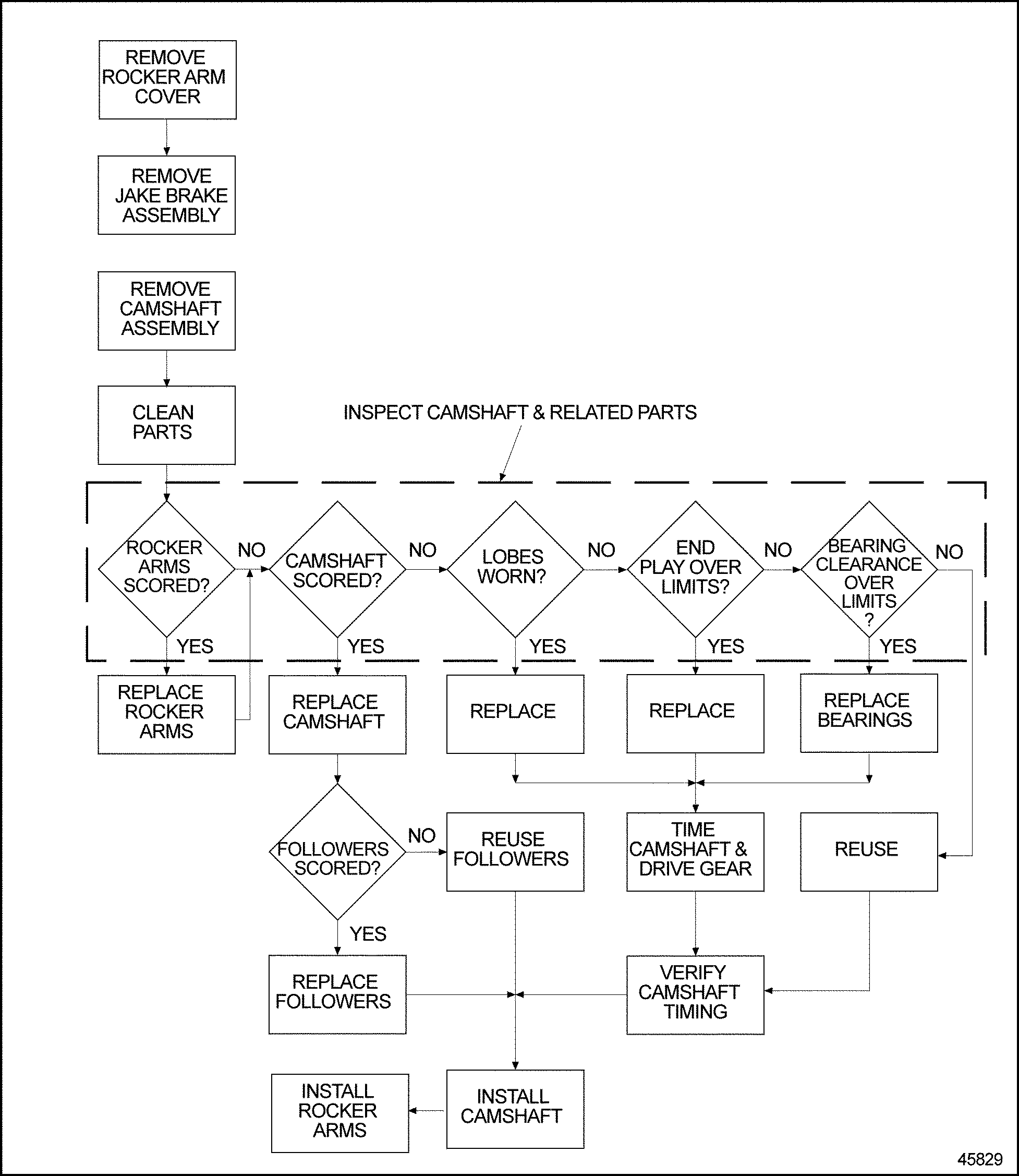
Figure 7. Flowchart for Repair or Replacement of Camshaft Gear Assembly
Section 1.26.2
Removal of Camshaft Gear Assembly
Remove camshaft gear assembly as follows:
- Install the crankshaft timing pin (J–45947)
into bracket and rotate the engine over by hand until the timing pin drops into the locating hole in the crankshaft, the engine is now at TDC on cylinder No.1. See Figure
"Crankshaft Timing Pin"
.

1. Timing Pin
Figure 8. Crankshaft Timing Pin
- Remove the valve rocker cover. Refer to "1.6.2 Removal and Cleaning of One-piece Rocker Cover For Diesel Engines Only" (one-piece), section "1.6.3 Removal and Cleaning of Two-piece Rocker Cover For Diesel Engines Only" (two-piece), and section "1.6.5 Removal and Cleaning of Three-piece Rocker Cover" (three-piece).
- Remove Jake Brake® assemblies refer to "1.36 Jake Brake" .
- Remove the five bolts for the camshaft gear cover inspection plate and remove the plate. See Figure
"Gear Case Assembly Cover"
.
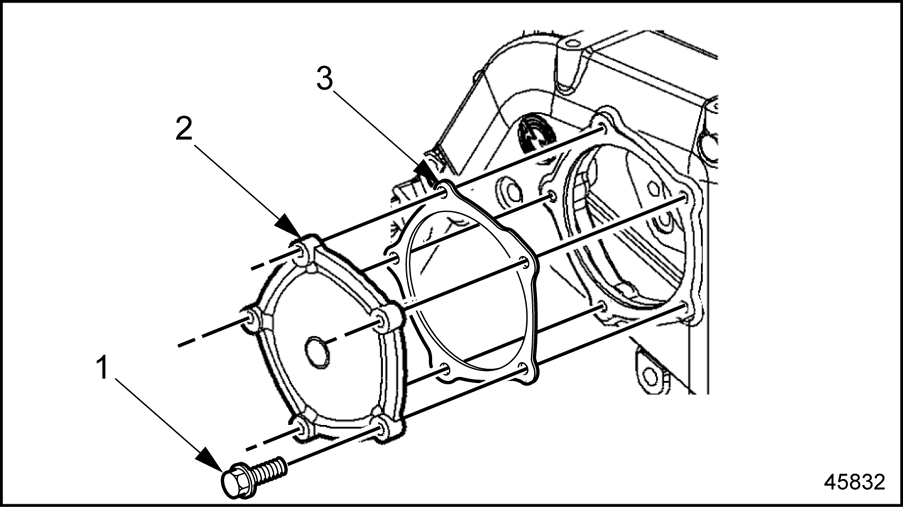
1. Bolt
3. Gasket
2. Cover
Figure 9. Gear Case Assembly Cover
- Remove Synchronous Reference Sensor/Crankshaft Position Sensor (SRS/CMP).
- Verify camshaft timing as follows:
- Look at the timing hole in the camshaft gear.
- The timing hole should be aligned with the timing hole in the back of the gear cover, located at the 5 o'clock position. See Figure "Timing Verification" .
- If the timing holes are not aligned correctly remove the crankshaft timing pin and rotate the engine one more complete revolution . When the timing pin drops back into the hole in the crankshaft check the timing of the camshaft. Refer to steps 6a
and 6b
.
1. Camshaft Gear Cover
2. Timing Hole
Figure 10. Timing Verification
- Remove bolt from front of camshaft gear cover. See Figure
"Camshaft Gear Cover Bolt"
.

1. Bolt
2. Camshaft Gear Cover
Figure 11. Camshaft Gear Cover Bolt
Note: If timing is correct and the repair being made does not require that the engine is turned over, clean off an area where the camshaft gear and idler gear teeth mesh and mark the teeth with a suitable marker for a reference point when reassembling the camshaft. This procedure will make assembly easier.
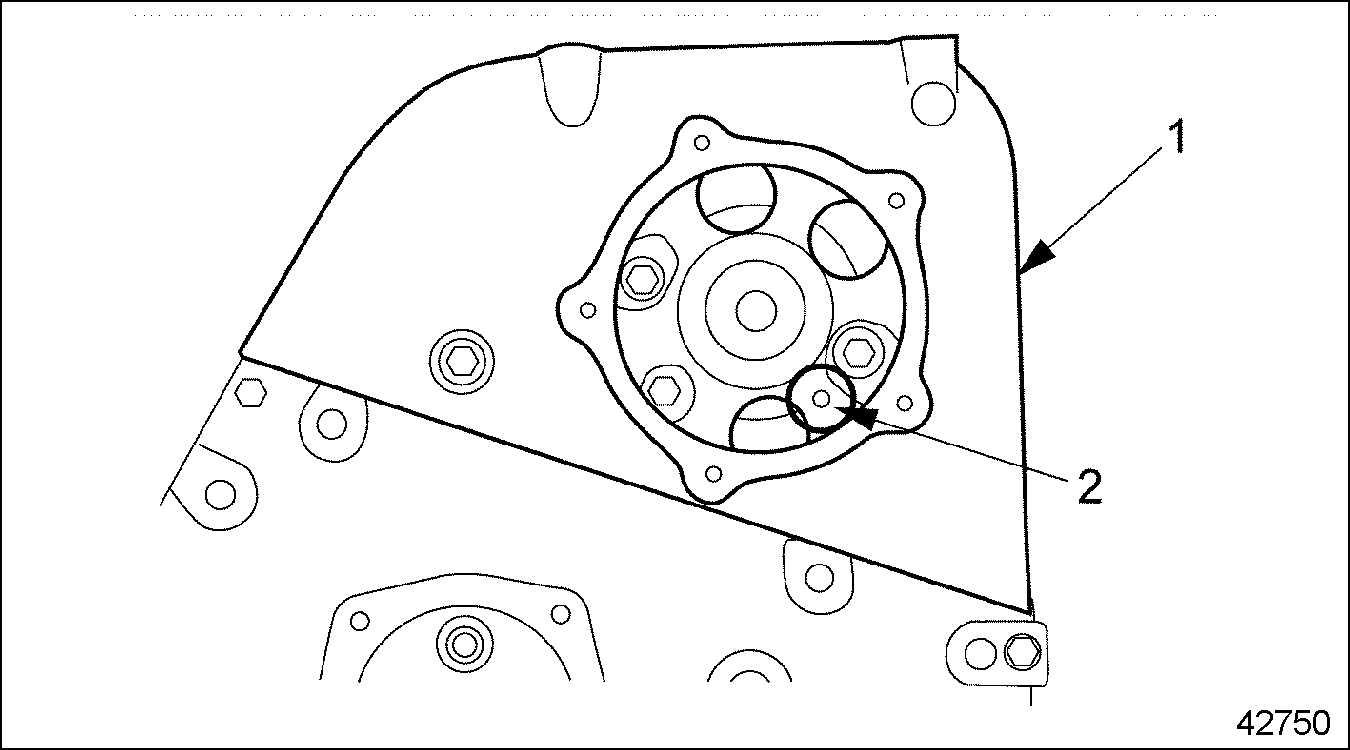
- Remove four camshaft gear cover bolts (1). See Figure
"Camshaft Gear Cover Bolts"
.
1. Bolt
Figure 12. Camshaft Gear Cover Bolts
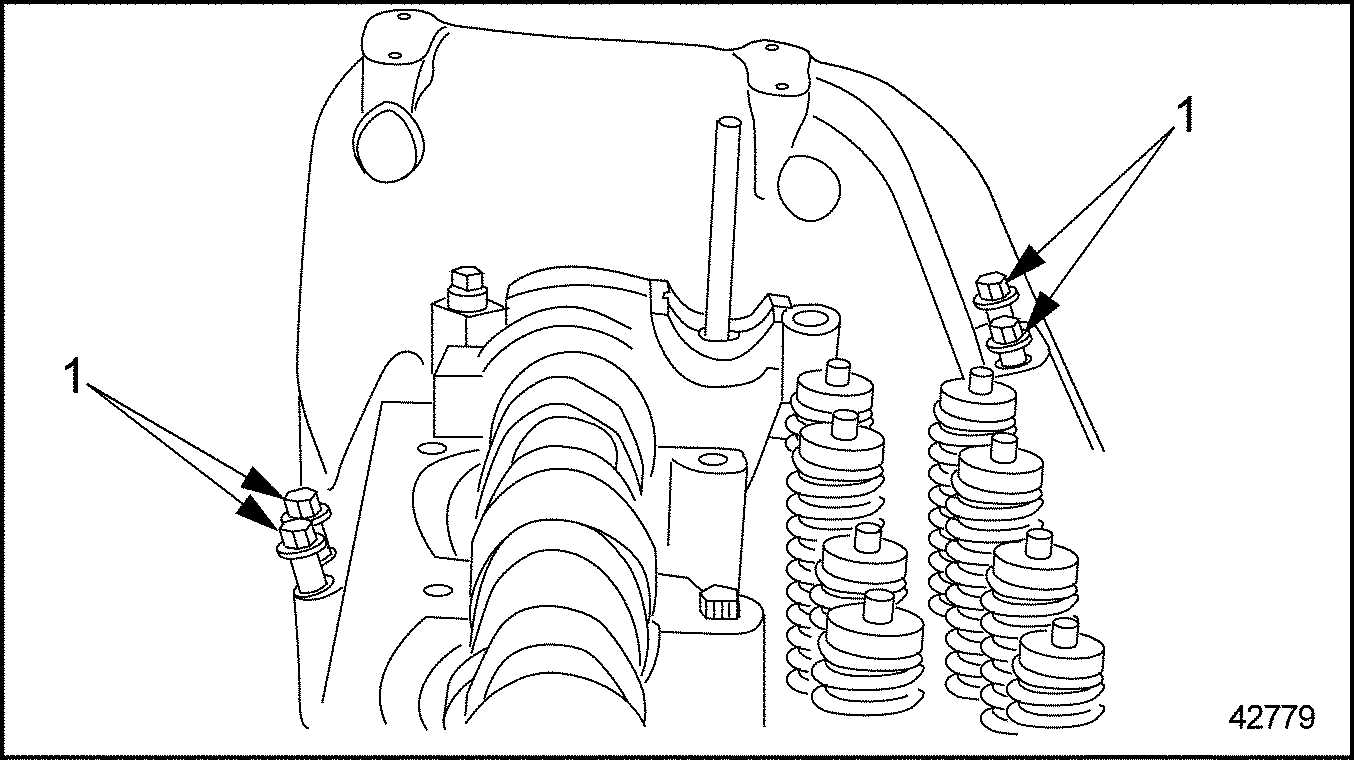
- Remove three bolts (1) inside of camshaft gear cover. See Figure
"Camshaft Gear Cover Bolts"
.
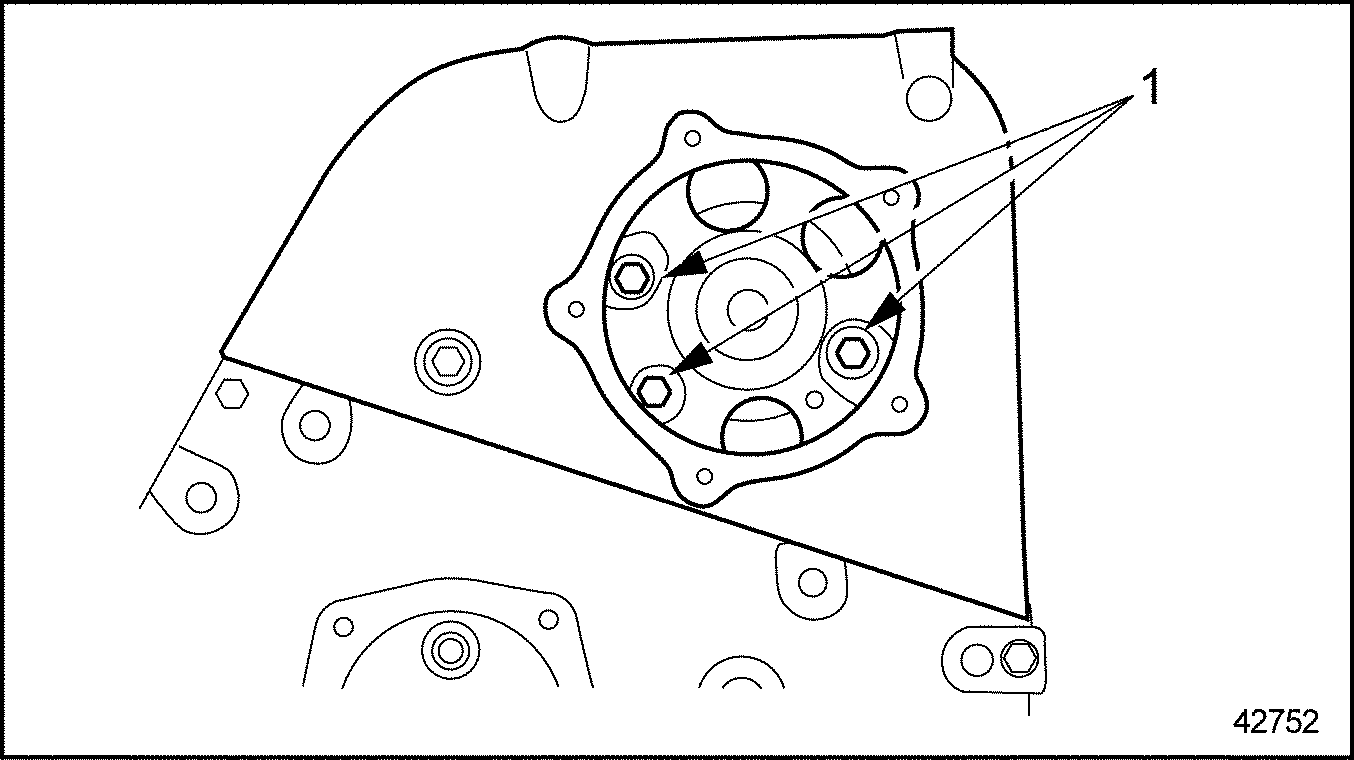
Figure 13. Camshaft Gear Cover Bolts
1. Bolt
- Remove one camshaft cap bolt and using socket tool ( J–44706)
and one stud bolt from camshaft caps No. 1 and 7, remove camshaft caps. See Figure
"Camshaft Cap Bolt and Stud Bolt"
and see Figure
"Camshaft Cap Stud Removal"
.
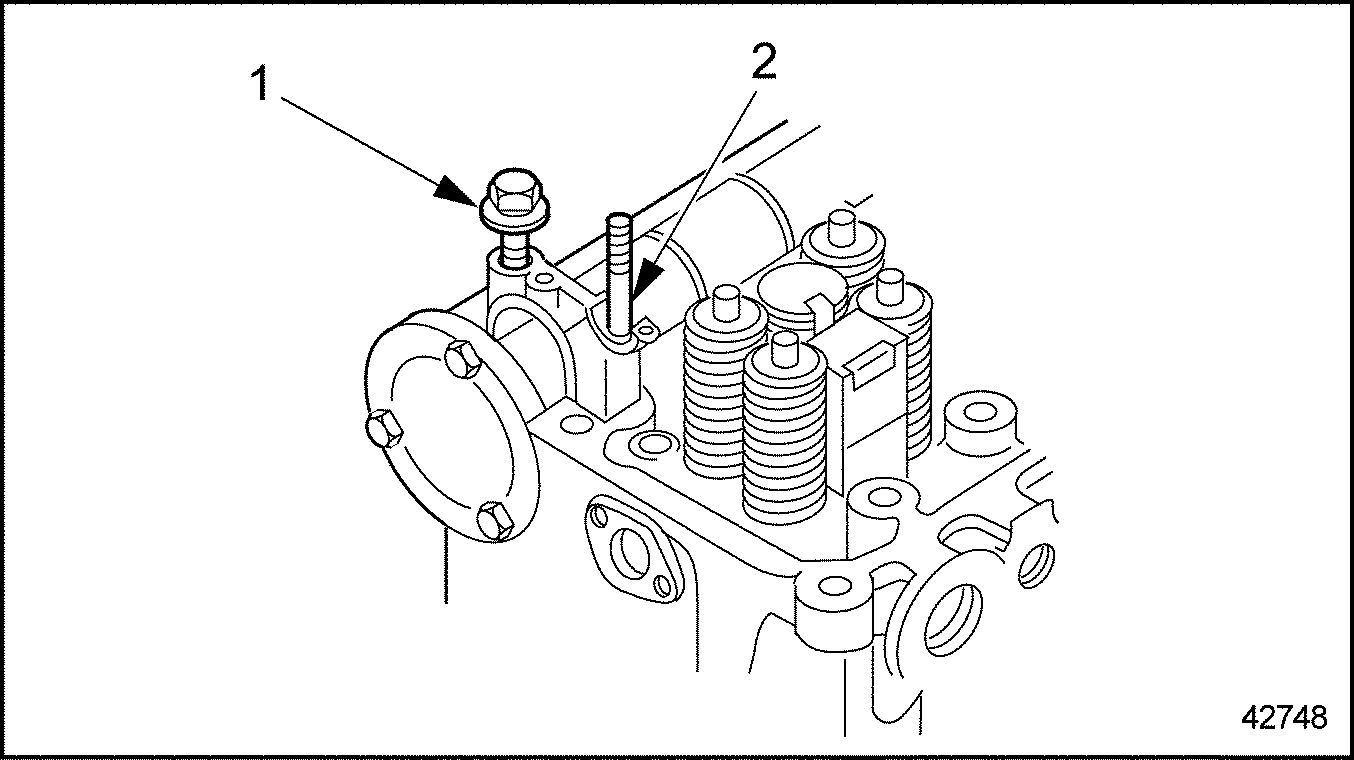
1. Bolt
2. Stud Bolt
Figure 14. Camshaft Cap Bolt and Stud Bolt

Figure 15. Camshaft Cap Stud Removal
- Remove the remaining five camshaft cap bolts, camshaft caps and upper bearing shells. Keep the caps and shells together for possible later installation Tag the bearing cap location, as they must always be installed in the same location.

PERSONAL INJURY
To avoid injury when removing or installing a heavy engine component, ensure the component is properly supported and securely attached to an adequate lifting device to prevent the component from falling.
- Lift camshaft and camshaft gear cover assembly from camshaft bearings and gear case. Use lifting tool (J–46305)
to assist in lifting camshaft gear cover assembly. See Figure
"Camshaft Gear Assembly and Lifting Tool"
.
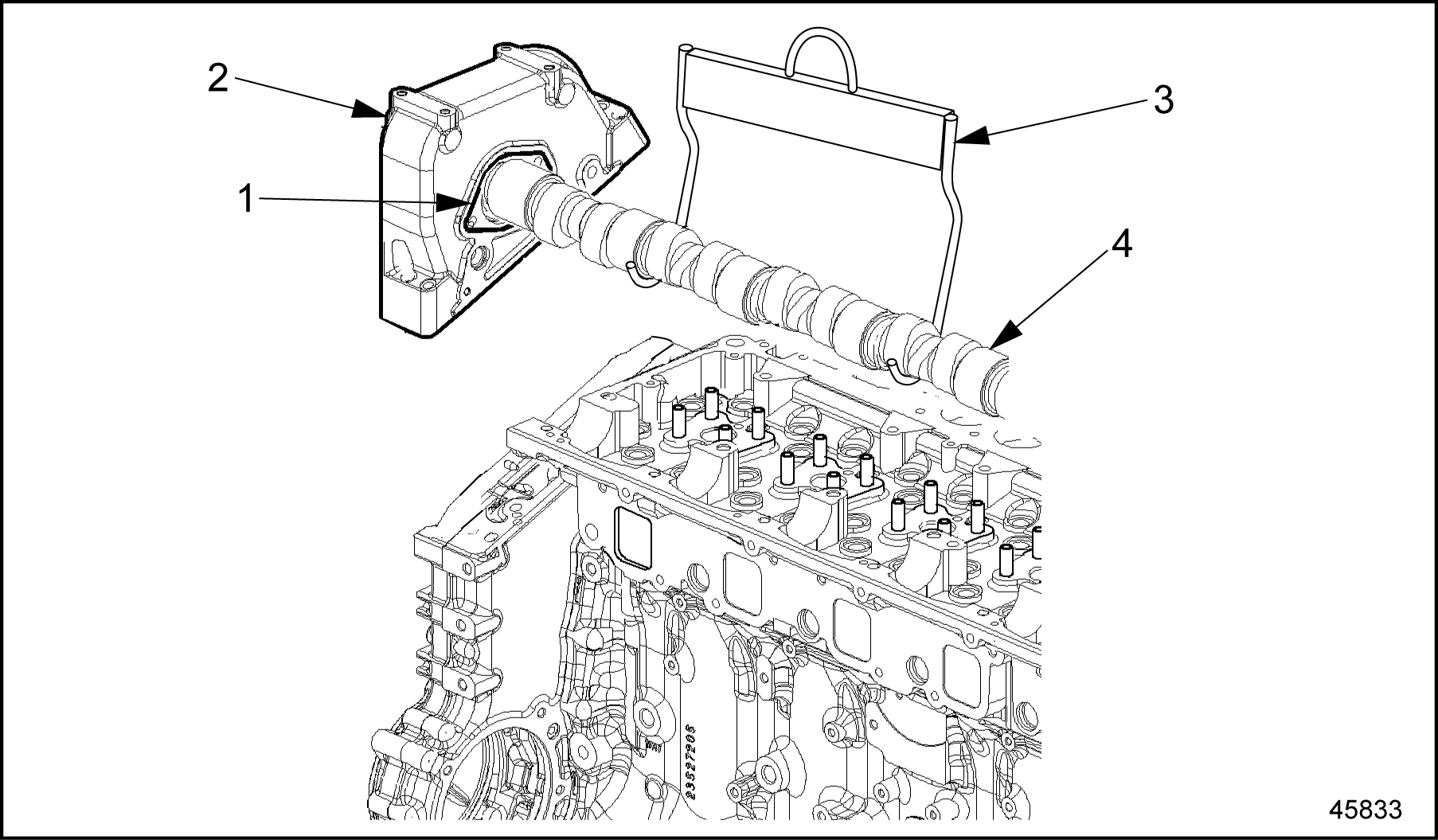
1. Seal
3. Lifting Tool
2. Camshaft Gear Cover
4. Camshaft
Figure 16. Camshaft Gear Assembly and Lifting Tool
- Remove the lower camshaft bearing shells, and group them with the upper shells and caps for possible reuse.
Section 1.26.3
Disassembly of Camshaft Gear Assembly EGR Model
Disassemble the camshaft from the camshaft gear as follows.
- Use suitable fixture to secure the camshaft assembly from movement.
- Install a heavy-duty gear puller capable of withstanding 48260 kPa (7000 psi) required to remove the gear from the camshaft. Support the backside of the camshaft gear cover as close to the camshaft as possible to prevent damaging the gear cover. Gently press the camshaft off the gear holding the camshaft as it is pressed through the gear. Remove the camshaft gear and gear cover together.
NOTICE
Extreme care must be taken not to support the camshaft gear cover at the outer edges.
Section 1.26.3.1
Inspection of Camshaft Gear Assembly and Camshaft Bearing
Inspect camshaft and camshaft bearings as follows:
- Clean all of the removed parts in clean fuel oil.

EYE INJURY
To avoid injury from flying debris when using compressed air, wear adequate eye protection (face shield or safety goggles) and do not exceed 276 kPa (40 psi) air pressure.
- Dry with compressed air.
- Inspect the rocker arm components for scoring. Refer to "1.3.2.2 Inspection of Rocker Arm Assemblies and Camshaft Lobes" .
- Replace damaged rocker arm components.
- Inspect the camshaft lobes and journals for scoring, pitting, or flat spots.
Note: Camshafts may exhibit surface pits on the exhaust lobes. See Figure "Camshafts Acceptable for Reuse" . Extensive durability and field testing has shown that surface pits on the exhaust lobes can occur early in the operation of the engine. These blemishes do not adversely affect engine performance or the durability of the camshaft and followers. Camshafts with this condition may be reused.
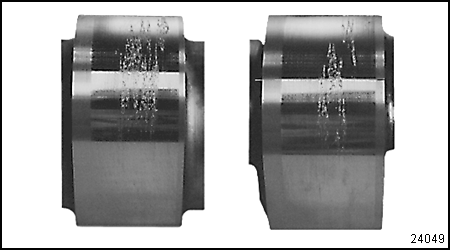
Figure 17. Camshafts Acceptable for Reuse
Note: Camshafts exhibiting extensive wear and pitting must be replaced. See Figure "Camshafts Not Acceptable for Reuse" .
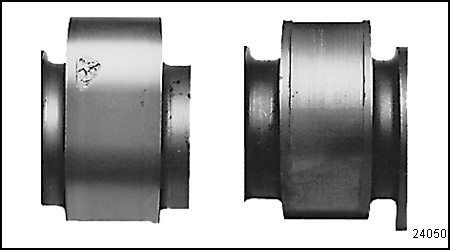
Figure 18. Camshafts Not Acceptable for Reuse
- If the camshaft is scored, inspect the camshaft follower rollers.
- Replace damaged camshaft followers.
- If there is a doubt as to the acceptability of the camshaft for further service, determine the extent of camshaft lobe wear as follows:
Note: The camshaft can be in or out of the engine during this procedure.
- Using a feeler gage, 0.038-0.254 mm (0.0015 -0.010 in.) and a piece of square, hard material 3 x 10 x 25 mm (1/8 in. x 3/8 in. x 1 in.), measure the flat on the injector rise side of the camshaft lobes and nose of valve lobes.See Figure "Checking Camshaft Lobe Wear" .
- If the flats measure greater than 0.076 mm (0.003 in.) in depth and there are no other camshaft defects, replace the camshaft.
- Inspect the camshaft bearings for signs of excessive wear, scoring or pitting.
- Replace camshaft bearings as necessary.
- Check the camshaft bearing clearance using plastic gaging material under each upper shell.
- Allowable clearance is 0.09 - 0.166 mm (0.0035 -0.0065 in.) or a maximum of 0.191 mm (0.0075 in.) with used parts.
- Replace excessively worn or scored parts.
- After completing the camshaft bearing clearance measurements, remove the rocker arm shafts, bearing caps, camshaft, and camshaft bearings. Keep the caps and shells together for possible reuse.
- Clean all of the plastic gaging material from the bearing shells and camshaft journals if used parts are to be reused.
- Remove all of the Gasket Eliminator from both the cylinder head and camshaft caps. Refer to "Cleaning" in the "General Information" section at the beginning of this manual.
- Coat the No. 1 and 7 bearing shell inserts with clean engine oil and install them to their respective locations in the cylinder head and camshaft caps.
- Install the camshaft to its normal position in the bearing saddles. Install the No. 1 and 7 camshaft caps to the cylinder head.
- Install the No. 1 and 7 camshaft cap outboard bolts and inboard studs and torque, using socket tool (J–44706) to the studs to 128–148 N·m (94–109 lb·ft).
- Using a dial indicator with magnetic base, check the run-out of the camshaft at the No. 4 bearing journal. See Figure "Camshaft Run-out Measurement" .
- If camshaft run-out exceeds 0.050 mm (0.002 in.), replace the camshaft.

Figure 19. Checking Camshaft Lobe Wear
Note: If one camshaft bearing needs to be replaced, replace both of the camshaft bearing shells.
Note: Check camshaft bearing clearance with bearing shells, camshaft, bearing caps and rocker arm shafts (without rocker assemblies in place) installed, and cap bolts, studs and nuts tightened to specification.

Figure 20. Camshaft Run-out Measurement
Section 1.26.4
Assembly of Camshaft Gear Assembly
Install the camshaft gear to the camshaft as follows:
|
|
|
To avoid injury from flying debris when using compressed air, wear adequate eye protection (face shield or safety goggles) and do not exceed 40 psi (276 kPa) air pressure. |
Note: If a new camshaft is being installed, steam clean it to remove the rust preventive and blow dry with compressed air.
- Using a suitable press, support the camshaft securely on the press. The bottom of camshaft must be firmly secured to prevent any movement.
- Install the camshaft gear into the camshaft gear cover and lower it as a assembly onto the nose of the camshaft.
- Align the key in the camshaft with the key way in the camshaft gear.
- Gently press the gear all the way onto the camshaft until it bottoms and is fully seated on the camshaft.
Section 1.26.5
Installation of Camshaft Bearings and Camshaft Gear Assembly
Install the camshaft bearings and camshaft gear assembly as follows:
Note: If new bearings are to be installed, the upper and lower shells MUST be replaced as a set.
- Coat the lower camshaft bearing shells with clean engine lubricating oil, and install them to their original positions. Note the position of oil holes and locating tangs.
- Coat the lobes and journals of the camshaft with clean engine lubricating oil.
- Install camshaft alignment tool (J–45946)
into camshaft gear cover and camshaft gear, making sure the pin on the tool is entered into the timing hole in the back of the camshaft gear cover. See Figure
"Camshaft Alignment Tool "
.
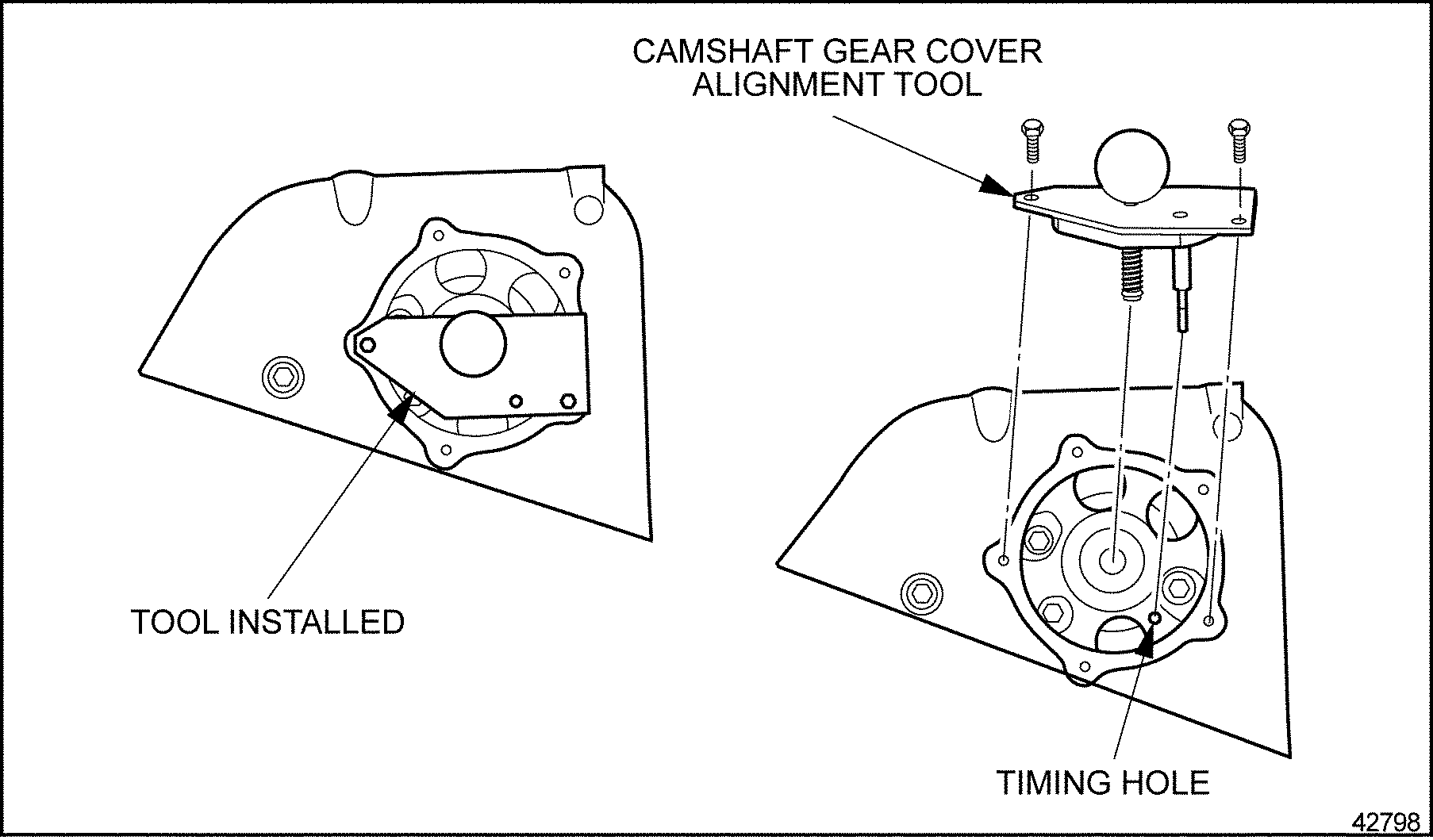
Figure 21. Camshaft Alignment Tool
NOTICE:
Do not bar the engine over with the timing pin installed. The timing pin will break.
- Ensure the timing pin is installed in the bracket on the front gear case cover and into crankshaft timing hole. See Figure
"Crankshaft Timing Pin"
.

1. Timing Pin
Figure 22. Crankshaft Timing Pin
- If the adjustable idler gear was removed or replaced, remove the cover plate and loosen the three hub retaining nuts so the gear hub can be easily moved. Install the centering tool (J–46306–A)
to hold idler gear hub at the middle of travel This procedure will assist in correctly installing the camshaft gear. See Figure
"Idler Gear Centering Tool J–46306–A"
.
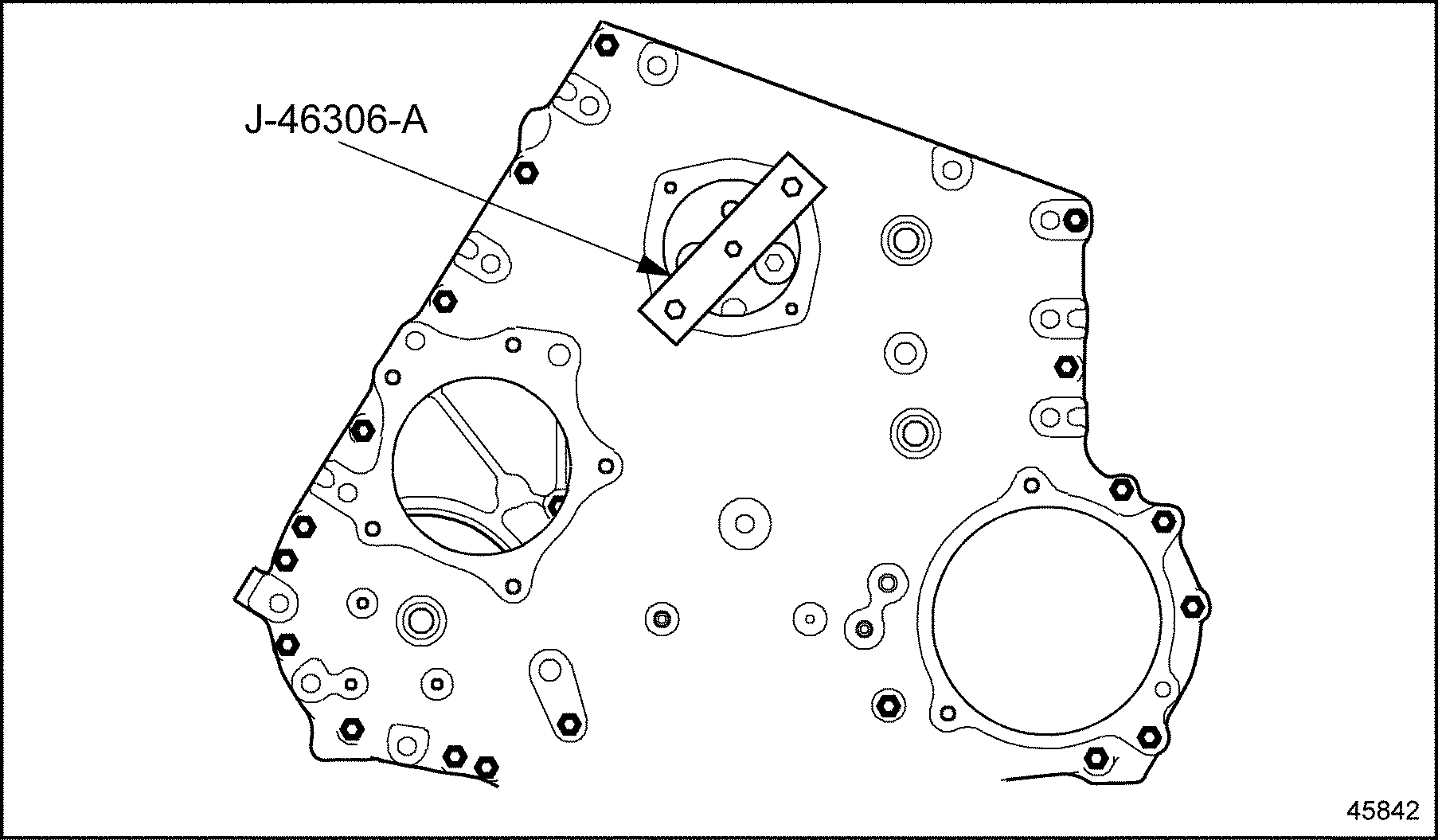
Figure 23. Idler Gear Centering Tool J–46306–A
- Ensure two seals are properly installed in camshaft gear cover. See Figure
"Camshaft Cover Seals"
.

Figure 24. Camshaft Cover Seals
- Apply RTV sealant along split line on gear case. See Figure
"Application of RTV Sealant along Split Line"
.
1. RTV Sealant
4. Lifting Tool J–46305
2. Seal
5. Camshaft
3. Camshaft Gear Cover
Figure 25. Application of RTV Sealant along Split Line
Note: Camshaft gear cover assembly must be installed promptly to avoid the setting of the RTV sealant .

PERSONAL INJURY
To avoid injury when removing or installing a heavy engine component, ensure the component is properly supported and securely attached to an adequate lifting device to prevent the component from falling.
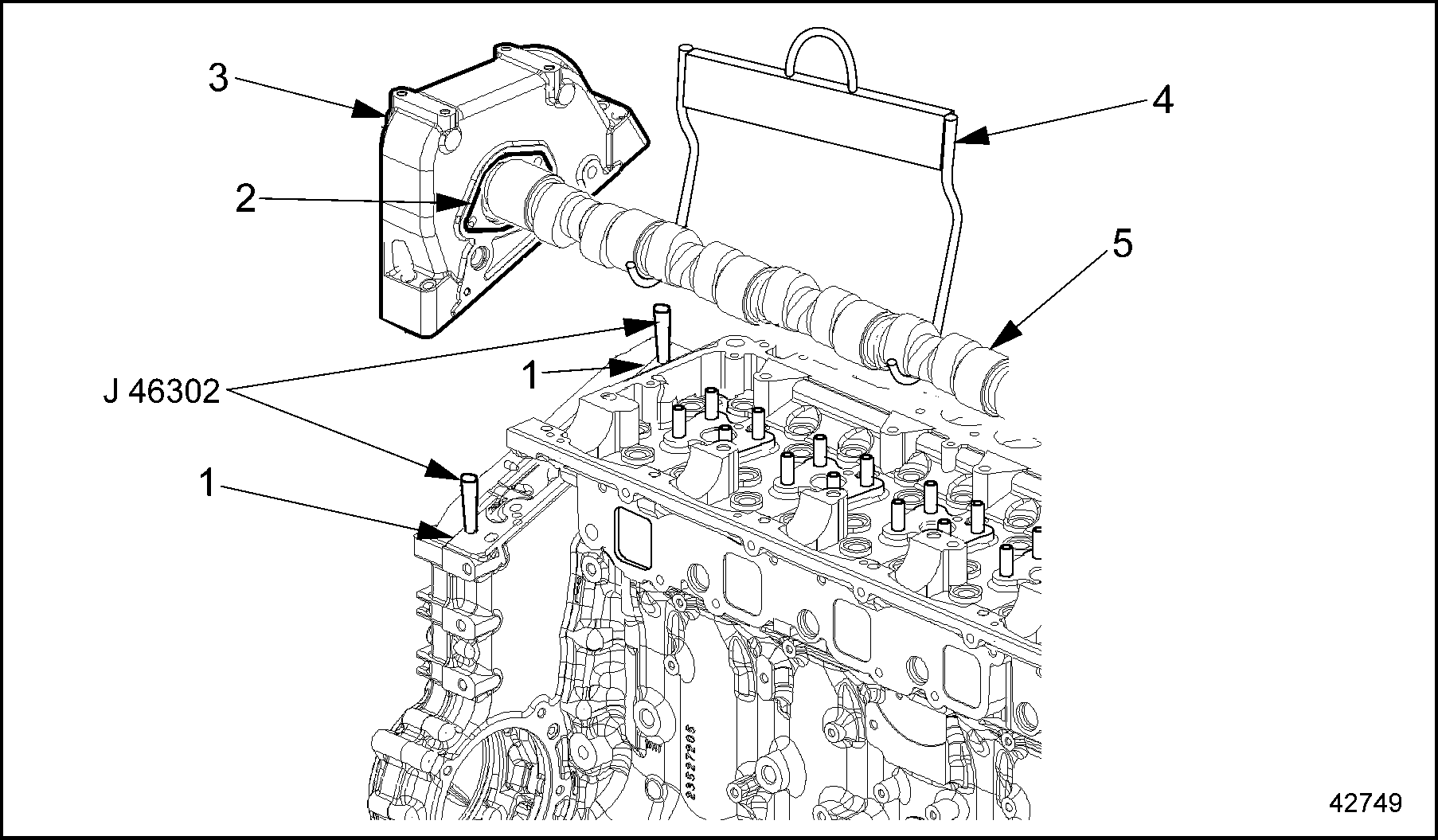
- Install two guide studs (J–46302) into gearcase to guide camshaft gear cover assembly onto gear case. Using lifting tool (J–46305), place front lifting hook between the number two injector lobe and intake valve and the rear hook between number four injector lobe and intake valve.
- Lower camshaft assembly into position on bearings and gear case. See Figure
"Application of RTV Sealant along Split Line"
.
Note: Insure that the seal on the rear of the camshaft gear cover does not catch on the edge of the cylinder head.
- When the assembly is in position remove the guide studs, install and hand tighten the four camshaft gear cover bolts until the camshaft gear cover just contacts the gear case do not torque.
- Remove the alignment tool, the timing hole in the back of the camshaft gear cover should be visible in the center of the hole in the gear. Reinstall the alignment tool to verify timing is correct. If timing is correct proceed to step 12
.
Note: Verify alignment tool is installed correctly. Incorrect installation will result in gear not being in time and the procedure will need to be repeated.

1. Camshaft Gear Cover
2. Timing Hole
Figure 26. Timing Verification
NOTICE:
Ensure RTV sealant is applied to camshaft cap No. 1 to prevent oil leaks and Gasket Eliminator® is applied to cap No. 7.
- Apply RTV to grooves in camshaft cap No.1 and Gasket Eliminator® to camshaft cap No. 7. See Figure
"Sealant Application"
.
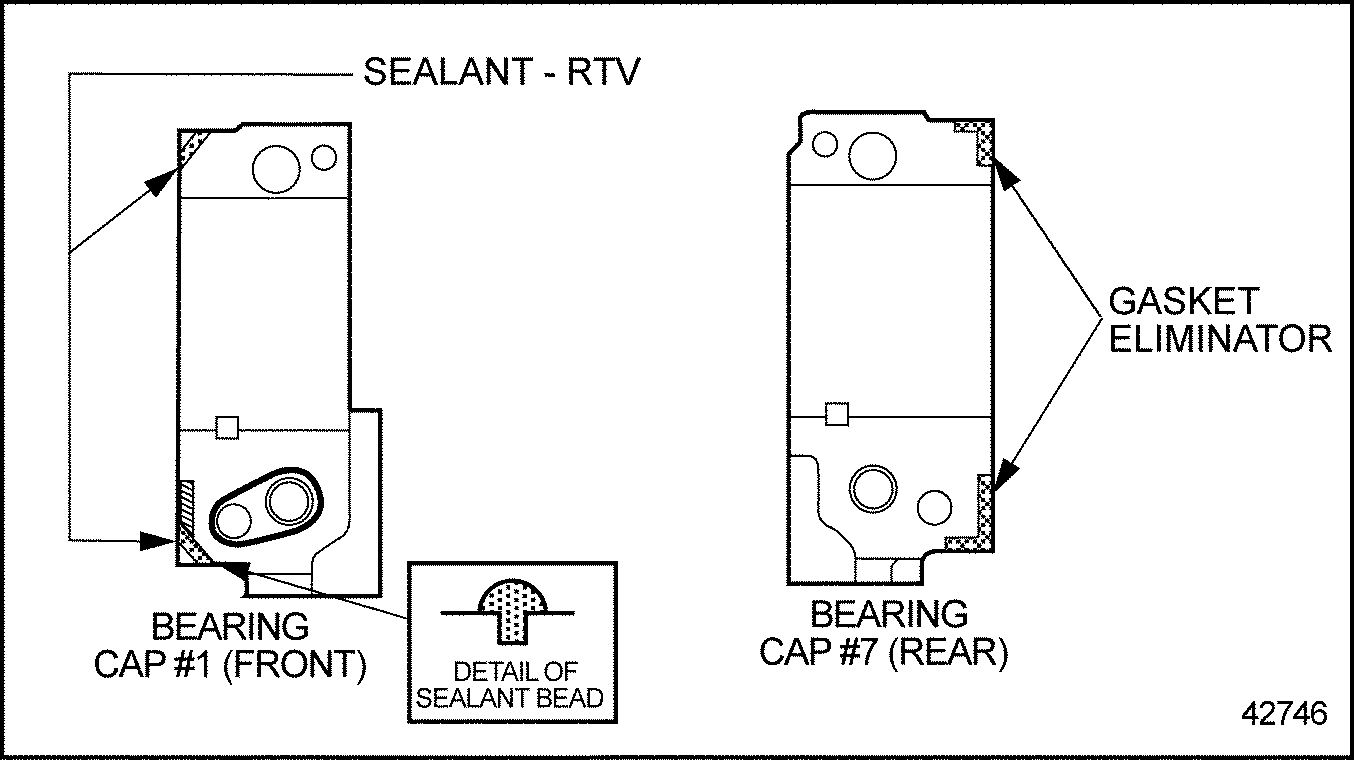
Figure 27. Sealant Application
NOTICE:
If the camshaft gear cover bolts and/or the camshaft cap bolts are tightened down with the camshaft gear out of time damage to the camshaft gear cover and the timing pin will result.
- Install No. 1 and 7 camshaft bearing caps with one bolt and one stud bolt in each and hand tighten. See Figure
"Camshaft Bearing Cap Bolt and Stud Bolt"
.

1. Bolt
2. Stud Bolt
Figure 28. Camshaft Bearing Cap Bolt and Stud Bolt
- Install the the remaining five camshaft caps in the following sequence; caps 3, 6, 2, 5 and 4. Hand tighten to prevent seal damage to the backside of the camshaft cover.
- Install three bolts inside camshaft gear cover, hand tighten to prevent seal damage.
- To seat the cover, torque the three inside camshaft gear cover bolts to 10 N·m (7 ft·lb).
- Torque camshaft cover bolts to 56-66 N·m (44-48 lb·ft) using torque sequence as shown in Figure
"Bolt Torque Sequence"
.
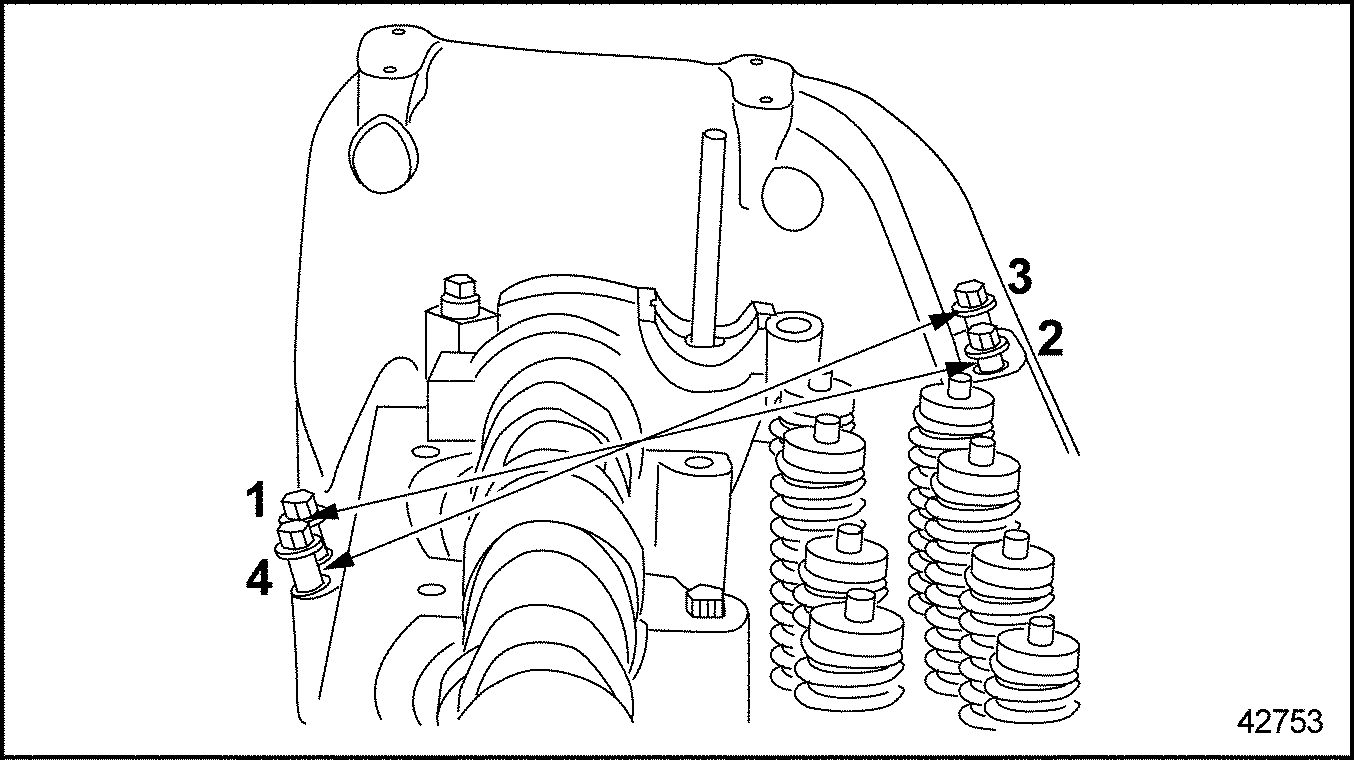
Figure 29. Bolt Torque Sequence
- Torque all camshaft cap bolts and stud bolts to 126-146 N·m (93-108 lb·ft).
- Torque the three bolts previously installed inside camshaft gear cover to 40 N·m (30 lb·ft). See Figure
"Camshaft Gear Cover Bolts"
.

1. Bolt
Figure 30. Camshaft Gear Cover Bolts
- Install remaining bolt to camshaft gear cover torque to 136 N·m (100 lb·ft). See Figure
"Camshaft Bolt"
.

1. Bolt
2. Camshaft Gear Cover
Figure 31. Camshaft Bolt
- Ensure timing of the gear has been verified. Refer to step 10 .
- Remove timing pin from crankshaft and alignment tool from gearcase cover.
- Check camshaft gear lash and adjust if necessary. Refer to "1.25.2.2 Engine Timing for the Compact Gear Train Assembly" .
- Torque idler gear nuts to 103-113 N·m (76-83 lb·ft).
- Install Synchronous Reference Sensor/Crankshaft Position Sensor (SRS/CMP).
| Series 60 Service Manual - 6SE483 |
| Generated on 10-13-2008 |